Introduction
In recent years, the rise of electric mobility has revolutionized the way we think about personal transportation. Among the most notable innovations in this sector are e-bikes, e-motorcycles, and e-scooters. These electric vehicles offer sustainable alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered transportation, combining environmental benefits with convenience and efficiency. This article provides an introduction to these electric modes of transport, exploring their features, benefits, and impact on urban mobility.
What Are E-Bikes?
Definition and Overview
An e-bike (electric bicycle) is a bicycle equipped with an electric motor that assists with propulsion. Unlike traditional bicycles, e-bikes have a battery-powered motor that provides a boost when pedaling, making it easier to tackle hills and long distances.

Key Components of E-Bikes
- Electric Motor: The motor provides power to assist with pedaling. It can be located in the hub of the wheel or within the bike’s frame.
- Battery: The battery stores electrical energy and powers the motor. It is usually removable for easy charging.
- Controller: The controller manages the power output from the battery to the motor, allowing riders to adjust the level of assistance.
- Pedal Assist and Throttle: Most e-bikes offer pedal assist, where the motor amplifies the rider’s pedaling effort. Some models also include a throttle for electric-only riding.
Types of E-Bikes
- City E-Bikes: Designed for urban commuting, city e-bikes often feature comfortable geometry, fenders, and racks for carrying cargo.
- Mountain E-Bikes: Built for off-road use, mountain e-bikes are equipped with rugged tires and suspension systems to handle rough terrain.
- Folding E-Bikes: These e-bikes can be folded for easy storage and transport, making them ideal for commuters with limited space.
What Are E-Motorcycles?
Definition and Overview
An e-motorcycle is a motorcycle powered entirely by electricity. Unlike e-bikes, e-motorcycles are designed for higher speeds and longer ranges, offering a more powerful alternative to traditional motorcycles.

Key Components of E-Motorcycles
- Electric Motor: The motor is typically more powerful than that of an e-bike, providing higher speeds and greater acceleration.
- Battery Pack: E-motorcycles are equipped with larger battery packs to support longer ranges and higher performance.
- Charging System: E-motorcycles come with fast-charging capabilities to minimize downtime and increase convenience.
- Regenerative Braking: Many e-motorcycles feature regenerative braking, which recovers energy during braking and extends the range.
Types of E-Motorcycles
- City E-Motorcycles: Designed for urban commuting, these motorcycles offer a balance of performance and efficiency for city travel.
- Sport E-Motorcycles: Built for high performance, sport e-motorcycles provide fast acceleration and top speeds for enthusiasts.
- Touring E-Motorcycles: These models are designed for long-distance travel, offering comfortable seating and extended range capabilities.
What Are E-Scooters?
Definition and Overview
An e-scooter (electric scooter) is a compact, electric-powered vehicle designed for short-distance travel. E-scooters are known for their portability and ease of use, making them a popular choice for urban commuters.

Key Components of E-Scooters
- Electric Motor: The motor is located in the wheel hub, providing power to propel the scooter.
- Battery: The battery is usually integrated into the scooter’s deck, providing power for its motor.
- Throttle: The throttle controls the scooter’s speed, allowing riders to accelerate and decelerate easily.
- Brakes: E-scooters are equipped with either disc brakes or drum brakes for safety and control.
Types of E-Scooters
- Commuter E-Scooters: Ideal for short commutes, these scooters are designed for efficiency and portability, often featuring lightweight frames and compact designs.
- Off-Road E-Scooters: Built for rugged terrain, off-road e-scooters feature larger tires and enhanced suspension systems.
- Folding E-Scooters: These e-scooters can be folded for easy storage and transport, making them convenient for urban users.
Benefits of Electric Mobility
Environmental Impact
One of the primary benefits of electric mobility is its environmental impact. E-bikes, e-motorcycles, and e-scooters produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and reliance on fossil fuels.
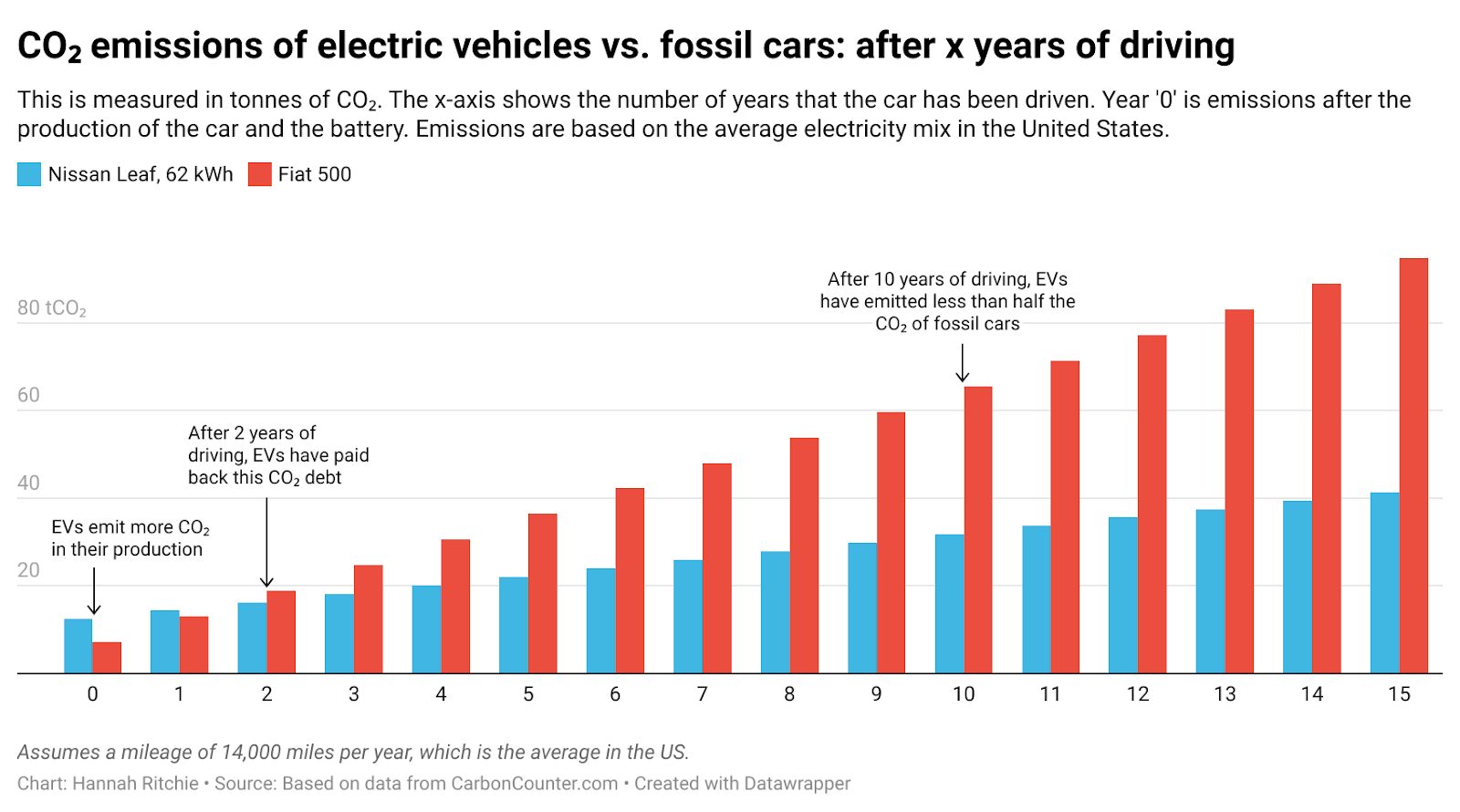
Cost Efficiency
Electric vehicles often have lower operating costs compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. Costs associated with charging are generally lower than refueling with gasoline, and electric vehicles require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts.
Convenience and Accessibility
Electric mobility solutions offer enhanced convenience for urban environments. E-bikes, e-motorcycles, and e-scooters can navigate traffic efficiently and are often allowed to use bike lanes, reducing commute times and improving accessibility.
Health and Wellness
For e-bikes, the pedal assist feature encourages physical activity while providing an extra boost for those who might otherwise find cycling challenging. E-scooters and e-motorcycles offer alternative modes of transport that can help reduce stress associated with heavy traffic.
Safety Considerations
Riding Gear and Equipment
Safety is paramount when riding e-bikes, e-motorcycles, and e-scooters. Riders should use appropriate protective gear such as helmets, gloves, and knee pads to reduce the risk of injury.

Traffic Laws and Regulations
Different regions have varying traffic laws and regulations for electric vehicles. It is important for riders to familiarize themselves with local regulations regarding the use of e-bikes, e-motorcycles, and e-scooters to ensure compliance and safety.
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance and care are essential to ensure the longevity and performance of electric vehicles. Regular checks of the battery, motor, and overall condition of the vehicle can help prevent issues and extend its lifespan.
The Future of Electric Mobility
Technological Advancements
The future of electric mobility is promising, with ongoing advancements in battery technology, motor efficiency, and charging infrastructure. Innovations in these areas are expected to enhance the performance, range, and convenience of electric vehicles.
Integration with Smart Cities
Electric mobility solutions are increasingly being integrated into smart cities, with initiatives aimed at improving urban transportation systems. This includes the development of charging networks, ride-sharing programs, and smart traffic management.
Conclusion
E-bikes, e-motorcycles, and e-scooters represent a significant shift towards sustainable transportation. These electric vehicles offer numerous benefits, including environmental advantages, cost efficiency, and enhanced convenience. As technology continues to advance, the adoption of electric mobility solutions is likely to increase, shaping the future of personal transportation.

FAQs
How long does it take to charge an e-bike, e-motorcycle, or e-scooter?
Charging times vary depending on the model and battery size. Generally, e-bikes take 3-6 hours to charge, while e-motorcycles and e-scooters can take 4-8 hours.
What is the range of an e-bike, e-motorcycle, or e-scooter on a single charge?
The range depends on the vehicle’s battery capacity and usage. E-bikes typically offer 20-60 miles, e-motorcycles 50-150 miles, and e-scooters 10-30 miles per charge.
Are e-bikes, e-motorcycles, and e-scooters legal to use in all areas?
Legality varies by region. Riders should check local regulations to ensure that their electric vehicle is compliant with local laws regarding usage, speed limits, and helmet requirements.
Can I use an e-bike, e-motorcycle, or e-scooter in the rain?
Most electric vehicles are designed to withstand light rain, but it’s best to avoid riding in heavy rain to prevent damage to the electrical components. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines for water resistance and maintenance tips.
How do I maintain my e-bike, e-motorcycle, or e-scooter?
Regular maintenance includes checking and charging the battery, inspecting the motor and drivetrain, and ensuring that tires and brakes are in good condition. Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations for optimal performance and longevity.
