Introduction
The transportation sector is undergoing a significant transformation, primarily driven by the rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). This shift towards electrification is not just reshaping automotive technology but is also profoundly impacting global energy consumption, urban planning, and environmental policies. This article explores how electric vehicles are changing the world, emphasizing their growing role in the future of transportation and their potential to address critical challenges such as climate change, air quality, and fossil fuel dependency.
The Rise of Electric Vehicles
Historical Context and Evolution
Electric vehicles are not a new concept; they have been around since the late 19th century. However, their development was overshadowed by gasoline-powered cars for decades. The resurgence of interest in EVs in the early 21st century was spurred by advances in battery technology, increased awareness of environmental issues, and governmental incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
Current Landscape
Today, the market for electric vehicles is growing exponentially. Major automakers are committing to electrifying their fleets, with companies like Tesla, Nissan, and Chevrolet leading the way, and luxury manufacturers like BMW, Audi, and Mercedes-Benz expanding their EV offerings. The increasing consumer interest, coupled with improvements in infrastructure such as charging stations, is rapidly making electric vehicles a common sight in cities around the world.

Impact on the Environment
Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
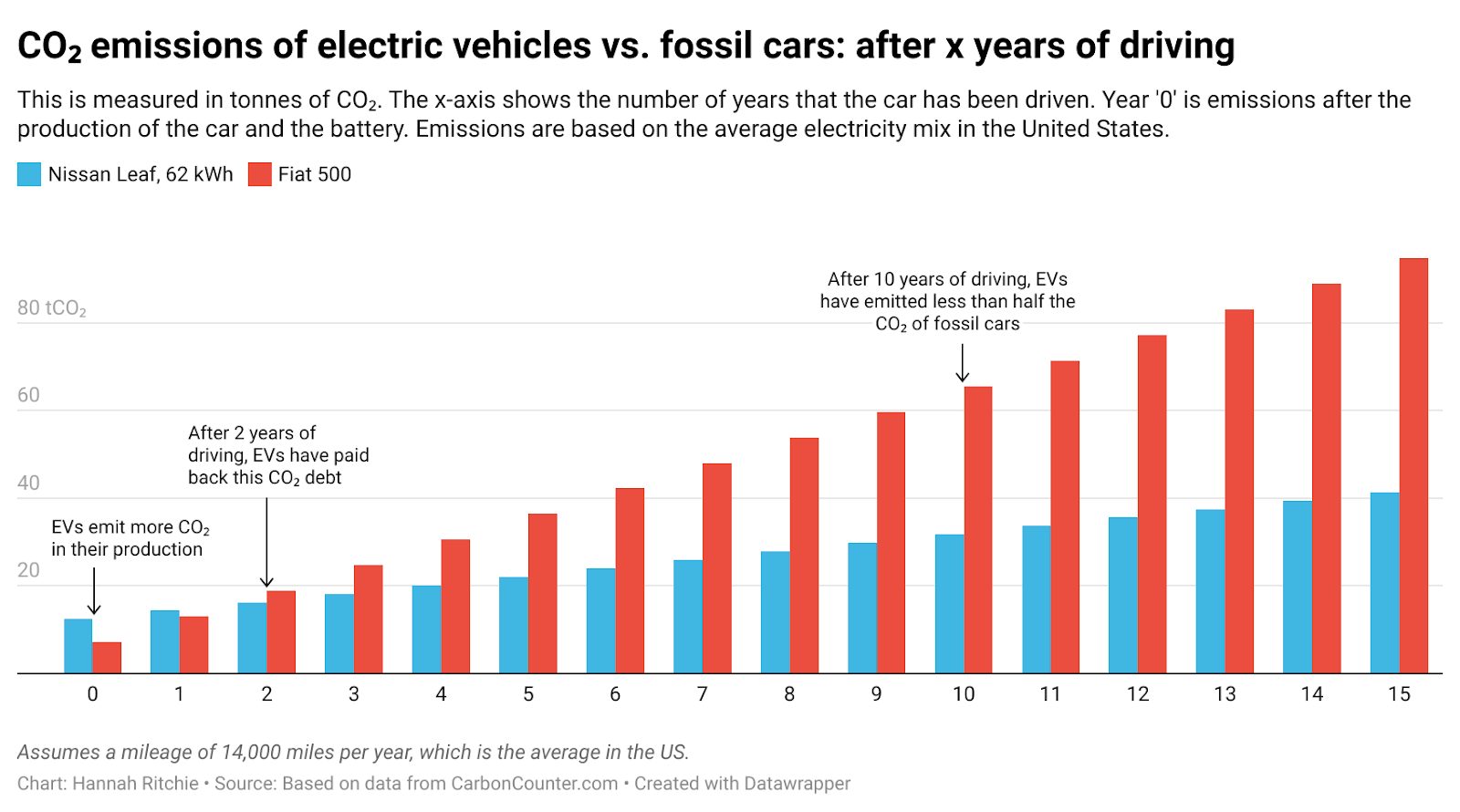
One of the most significant impacts of electric vehicles is their potential to reduce the emissions that contribute to climate change. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric vehicles produce no direct exhaust emissions, which means a substantial decrease in air pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen oxides.
Decreased Dependence on Fossil Fuels
Electric vehicles help reduce dependence on oil, diversifying energy sources with alternatives like nuclear, hydro, and renewable energies such as wind and solar. This not only helps in reducing the carbon footprint but also enhances energy security by reducing geopolitical risks associated with oil dependency.
Energy Efficiency
Electric vehicles are inherently more efficient than gasoline vehicles. They convert over 60% of the electrical energy from the grid to power at the wheels, compared to about 20% for gasoline vehicles. This efficiency translates into better performance and lower energy costs over the vehicle’s lifetime.
Technological Advancements Driving EV Adoption
Battery Technology
Advancements in lithium-ion battery technology have been crucial in making EVs more competitive. Improvements in energy density, safety, and cost have not only extended the range of electric vehicles but have also reduced their overall cost, making them more accessible to a broader audience.
Charging Infrastructure
The development of fast-charging technology and the expansion of charging networks are vital for widespread EV adoption. Innovations such as wireless charging and ultra-fast charging stations capable of charging batteries in minutes are expected to solve range anxiety and make electric vehicles even more appealing.
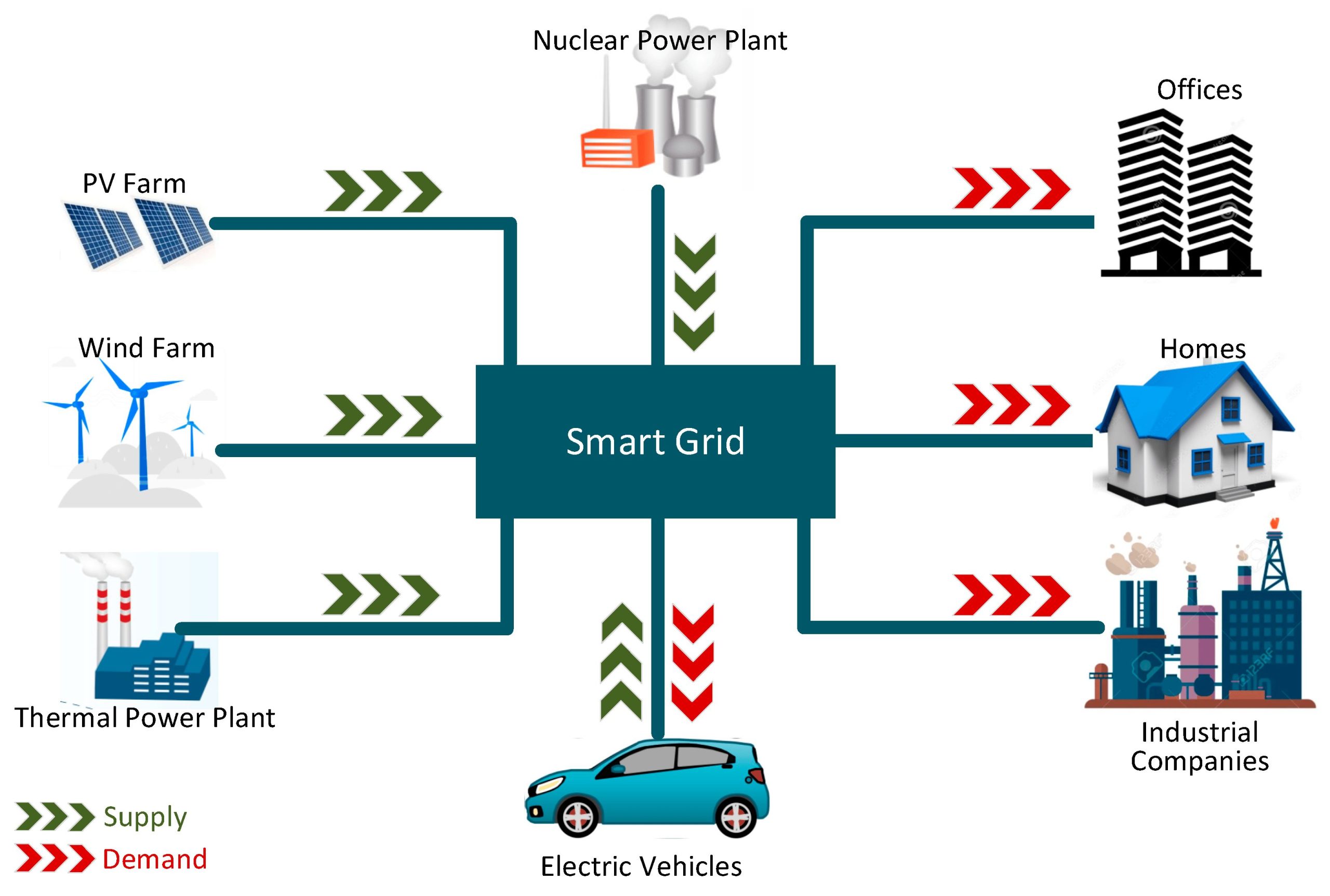
Integration with Smart Grids
Electric vehicles play a crucial role in the emergence of smart grids. With vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, EVs can interact with the power grid to return energy during peak demand or store excess power when demand is low. This not only enhances grid stability but also turns electric vehicles into mobile energy storage units.
Economic and Social Impacts
Job Creation and Industry Growth
The electric vehicle industry is a significant driver of economic growth, creating jobs in new and expanding sectors such as battery manufacturing, EV assembly, and charging infrastructure development. This shift is also fostering innovations in related areas, such as autonomous driving and mobility services.
Urban Planning and Public Health
The adoption of electric vehicles influences urban planning and public health. Cities are redesigning infrastructure to accommodate EVs, which leads to cleaner air and a quieter urban environment. This reduction in noise and air pollution directly benefits public health, reducing diseases associated with air quality and noise stress.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Market Challenges
Despite the rapid growth, the electric vehicle market faces challenges such as high initial costs, battery disposal and recycling issues, and the need for more substantial financial incentives to accelerate adoption rates.
The Road Ahead
Looking forward, the integration of EVs with renewable energy sources, advancements in battery technology, and supportive regulatory frameworks will be critical in realizing the full potential of electric vehicles. Continued innovation and investment will likely see EVs becoming the norm rather than the exception, leading the way toward a sustainable and efficient future of transportation.
Conclusion
Electric vehicles represent a pivotal shift in the future of transportation, offering not just an alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, but a transformative solution to many of the pressing environmental and economic challenges facing the world today. As technology continues to evolve and the benefits become even more apparent, the transition to electric vehicles is expected to accelerate, reshaping how we think about mobility, energy consumption, and environmental stewardship.
FAQs
What are the main advantages of electric vehicles over gasoline vehicles?
Electric vehicles offer numerous advantages over gasoline-powered vehicles, including:
- Lower emissions: EVs significantly reduce greenhouse gases and other pollutants.
- Energy efficiency: Electric engines are more efficient at converting energy into vehicle movement.
- Reduced energy dependence: EVs decrease reliance on petroleum and can be powered by diverse and renewable energy sources.
- Lower operating costs: Electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, and EVs require less maintenance.
How long do electric vehicle batteries last?
Modern electric vehicle batteries typically have a lifespan of about 8 to 10 years or between 100,000 and 150,000 miles, depending on the vehicle and usage patterns. Advances in battery technology continue to improve longevity and performance.
Are electric vehicles truly environmentally friendly?
Electric vehicles are generally more environmentally friendly than conventional vehicles due to their zero tailpipe emissions. However, the overall environmental impact depends on the sources of electricity used to charge the batteries and the methods used for battery production and disposal. Using renewable energy to charge EVs maximizes their environmental benefits.
What is the current state of the EV charging infrastructure?
The EV charging infrastructure is rapidly expanding globally, with significant investments from governments and private companies. Urban areas and major highways are increasingly being equipped with charging stations, including fast-charging technology that allows drivers to recharge their batteries in as little as 20 minutes.
How are electric vehicles changing urban planning?
Electric vehicles are influencing urban planning by requiring updates to infrastructure, such as increased availability of charging stations and integration into public transport systems. This shift encourages cities to adopt more sustainable practices, potentially reducing urban sprawl and promoting higher density, transit-oriented developments.
